(JAVA) 클래스로더

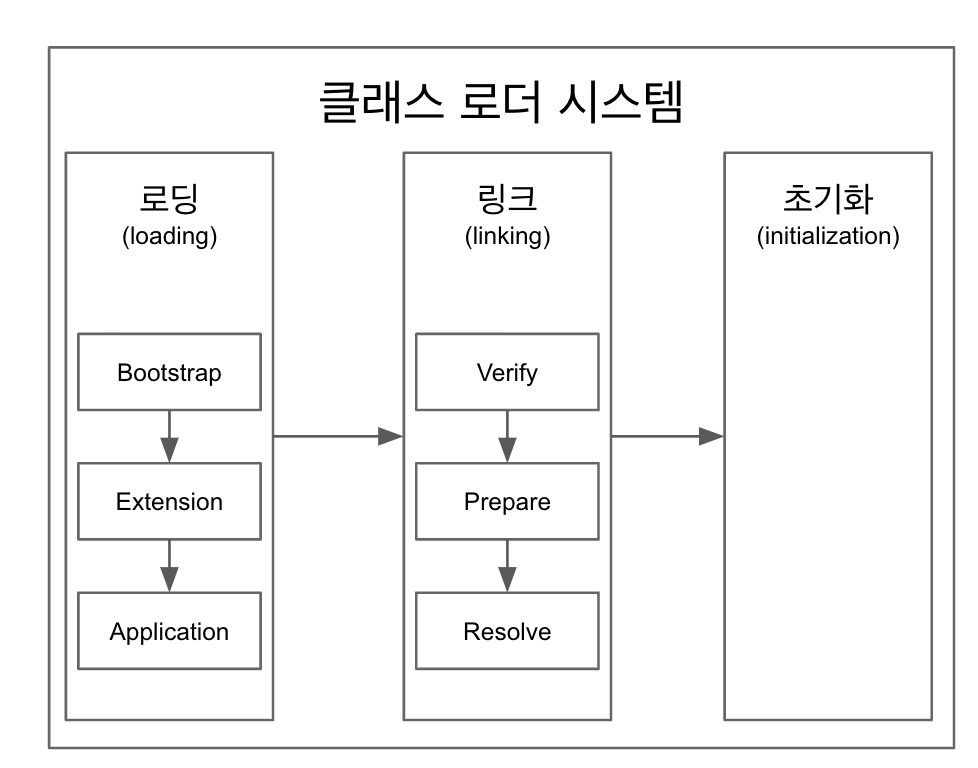
클래스 로더
-
로딩, 링크, 초기화 순으로 진행된다.
-
로딩
-
클래스 로더가 .class 파일을 읽고 그 내용에 따라 적절한 바이너리 데이터를 만들고 “메소드” 영역에 저장.
-
이때 메소드 영역에 저장하는 데이터
-
FQCN(풀 패키지 경로)
-
클래스 | 인터페이스 | 이늄
-
메소드와 변수
-
로딩이 끝나면 해당 클래스 타입의 Class 객체를 생성하여 “힙" 영역에 저장.
public class App
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
System.out.println(App.class.getClassLoader());
}
}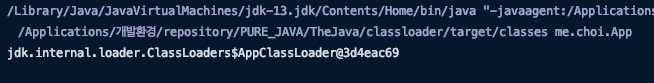
클래스로더는 계층형 구조이다.
public class App
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
ClassLoader classLoader = App.class.getClassLoader();
System.out.println("App class의 클래스로더");
System.out.println(classLoader);
ClassLoader parent = classLoader.getParent();
System.out.println("App class의 부모의 클래스로더");
System.out.println(parent);
ClassLoader grandMother = parent.getParent();
System.out.println("App class의 부모의 부모의 클래스로더");
System.out.println(grandMother);
}
}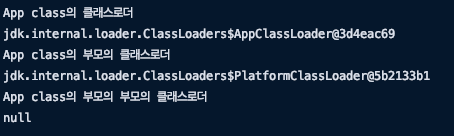
부모의 부모가 null이 나오는 이유는
부모의 부모인 부트스트랩 로더는 native로 작성된 클래스로더이기 때문에 자바코드로 출력 할 수 없다.
세개의 클래스로더의 내부구조
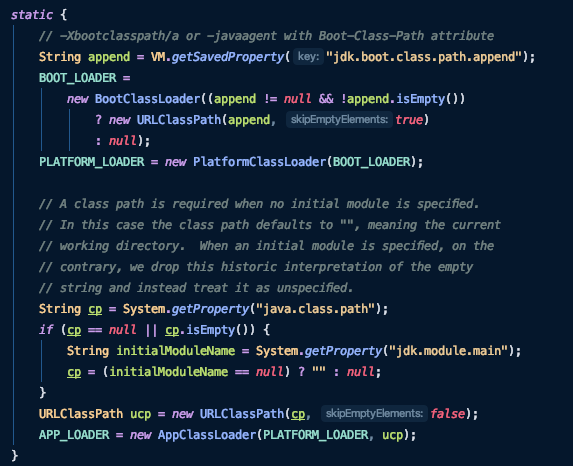
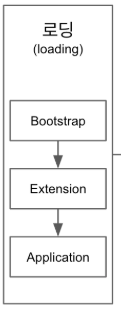
실행순서
할머니 - 엄마 - 자식
자식도 못 읽는 다면?
ClassNotFoundException 이 발생한다.
-
링크
-
Verify, Prepare, Reolve(optional) 세 단계로 나눠져 있다.
-
검증: .class 파일 형식이 유효한지 체크한다.
-
Preparation: 클래스 변수(static 변수)와 기본값에 필요한 메모리 (메모리를 준비하는 과정)
-
Resolve: 심볼릭 메모리 레퍼런스를 메소드 영역에 있는 실제 레퍼런스로 교체한다. (이 과정은 optional 이다.)
심볼릭 메모리 레퍼런스 : 코드에 나와있는 논리적인 레퍼런스 ex) Choi choi = new Choi();
실제 레퍼런스 : 힙에 올라와 있는 객체의 래퍼런스
-
초기화
-
Static 변수의 값을 할당한다. (static 블럭이 있다면 이때 실행된다.)
하지만! 제일 중요한 것은 바이트코드다.